中文名稱:兔抗COX7A2多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
Cytochrome c oxidase, the terminal component of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, catalyzes the electron transfer from reduced cytochrome c to oxygen. This component is a heteromeric complex consisting of three catalytic subunits encoded by mitochondrial genes, and multiple structural subunits encoded by nuclear genes. The mitochondrially-encoded subunits function in electron transfer, while the nuclear-encoded subunits may function in the regulation and assembly of the complex. This nuclear gene encodes polypeptide 2 (liver isoform) of subunit VIIa, with this polypeptide being present in both muscle and non-muscle tissues. In addition to polypeptide 2, subunit VIIa includes polypeptide 1 (muscle isoform), which is present only in muscle tissues, and a related protein, which is present in all tissues. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 4 and 14. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
COX7A2 |
|
Immunogen: |
Synthetic peptide of human COX7A2 |
|
Full name: |
cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A2 |
|
Synonyms: |
VIIAL; COX7AL; COX7AL1; COXVIIAL; COXVIIa-L |
|
SwissProt: |
P14406 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
5000-10000 |
|
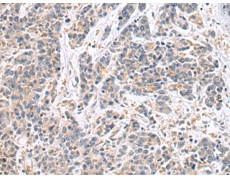
IHC positive control: |
Human colorectal cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-50 |
|
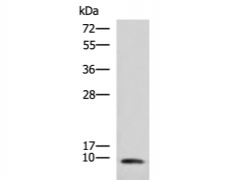
WB Predicted band size: |
9 kDa |
|
WB Positive control: |
Hela cell lysate |
|
WB Recommended dilution: |
200-1000 |


 購物車
購物車 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009