中文名稱(chēng):兔抗ZNF621多克隆抗體
|
Background: |
Zinc-finger proteins contain DNA-binding domains and have a wide variety of functions, most of which encompass some form of transcriptional activation or repression. The majority of zinc-finger proteins contain a Krüppel-type DNA binding domain and a KRAB domain, which is thought to interact with KAP1, thereby recruiting histone modifying proteins. As a member of the krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family, ZNF621 (Zinc finger protein 621) is a 439 amino acid nuclear protein that contains one KRAB domain and seven C2H2-type zinc fingers. The gene encoding ZNF621 maps to human chromosome 3, which is made up of about 214 million bases encoding over 1,100 genes, including a chemokine receptor (CKR) gene cluster and a variety of human cancer-related gene loci. Marfan Syndrome, porphyria, von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, osteogenesis imperfecta and Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease are a few of the numerous genetic diseases associated with chromosome 3. There are two isoforms of ZNF621 that are produced as a result of alternative splicing events. May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
|
Applications: |
ELISA, IHC |
|
Name of antibody: |
ZNF621 |
|
Immunogen: |
Fusion protein of human ZNF621 |
|
Full name: |
zinc finger protein 621 |
|
SwissProt: |
Q6ZSS3 |
|
ELISA Recommended dilution: |
2000-5000 |
|
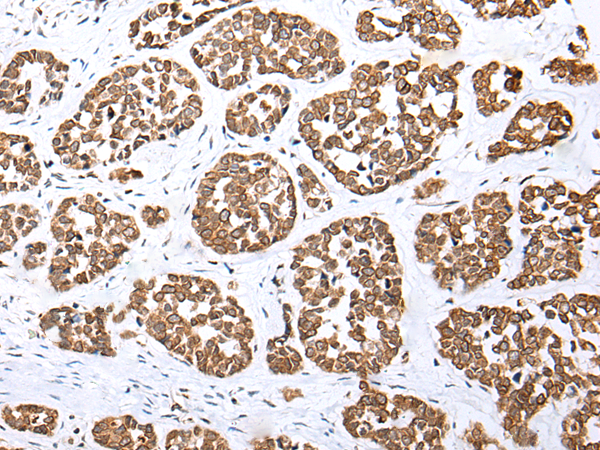
IHC positive control: |
Human esophagus cancer |
|
IHC Recommend dilution: |
25-100 |

 購(gòu)物車(chē)
購(gòu)物車(chē) 幫助
幫助
 021-54845833/15800441009
021-54845833/15800441009